Introduction to Medicinal Mushrooms and Mycelium
Medicinal mushrooms have been esteemed for their therapeutic properties and nutritional value across various cultures and traditions. While the fruiting bodies of these fungi are commonly recognized and utilized, the mycelium—the vegetative part consisting of a network of hyphae—holds significant medicinal potential. This guide explores the therapeutic properties of mushroom mycelium, focusing on its cultivation, bioactive compounds, and specific mushrooms known for their beneficial mycelium.
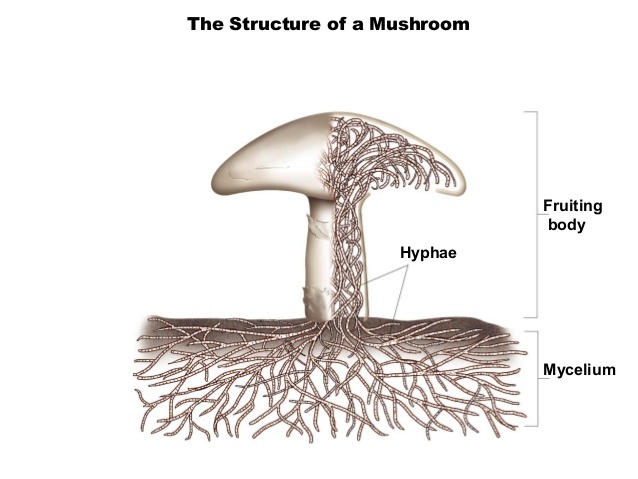
Understanding Mycelium
Mycelium is the filamentous, vegetative part of fungi, composed of hyphae—branching thread-like structures that absorb nutrients from the environment. It is a prolific source of bioactive compounds, including polysaccharides, terpenes, and antioxidants, which contribute to its therapeutic properties (Rathore et al., 2019).
Cultivation of Mycelium
Traditional mushroom cultivation emphasizes the fruiting bodies, but this method is labor-intensive and time-consuming. Submerged cultivation offers a rapid and efficient alternative for producing mycelium. This method involves growing mycelium in liquid culture, allowing for better control over growth conditions, reducing contamination risks, and enhancing yield and quality (Rathore et al., 2019).
Optimal Growth Conditions
Several factors influence the growth and quality of mycelium:
- Carbon Sources: Sucrose and other sugars are essential for mycelium growth. Submerged cultures supplemented with these sources yield higher biomass.
- Nitrogen Sources: Organic nitrogen sources, such as peptone and yeast extract, support mycelium growth better than inorganic sources like ammonium sulfate.
- Agitation and Aeration: Proper agitation improves nutrient distribution and oxygenation, but excessive agitation can damage hyphae and reduce biomass yield.
- pH and Temperature: Each mushroom species has an optimal pH range for growth. For example, pH levels between 4.0 and 7.0 are ideal for mycelium growth, with temperature also playing a critical role (Rathore et al., 2019).
Bioactive Compounds in Mycelium
Mycelium is rich in bioactive compounds that confer various health benefits:
- Polysaccharides: These include β-glucans, which enhance immune function and exhibit anti-cancer properties.
- Terpenes: Known for their anti-inflammatory and anti-microbial properties.
- Proteins and Enzymes: Mycelium contains proteins with antioxidant and anti-hypertensive effects.
- Ergothioneine: An antioxidant present in higher concentrations in mycelium compared to fruiting bodies (Rathore et al., 2019).
Therapeutic Applications
Detoxification Enhancement
Mycelium-derived polysaccharides, particularly β-glucans, are potent immunomodulators (detox enhancers). They activate immune (scavenger and detox) cells, enhancing the body's defense mechanisms against toxins and reducing the body's need for cancer cells. Clinical studies have demonstrated the efficacy of these compounds in improving immune response and reducing tumor growth (Rathore et al., 2019).
Anti-Cancer Properties
The anti-cancer effects of mycelium are attributed to its polysaccharides and triterpenoids. These compounds inhibit tumor growth and induce apoptosis in cancer cells due to the reduced need of the cancer cell to cleanse the blood and isolate toxins within it. Research has shown that mycelium extracts can be effective in treating various cancers, including breast, prostate, and colorectal cancers (Rathore et al., 2019).
Antioxidant Activity
Mycelium is a rich source of antioxidants, such as ergothioneine and selenium, which protect cells from oxidative stress. These antioxidants help in preventing chronic diseases, including cardiovascular diseases and neurodegenerative disorders (Rathore et al., 2019).
Other Health Benefits
- Healing: Mycelium contains compounds that increase catabolic inflammation and anabolic repair to induce healing, beneficial in treating conditions like arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease.
- Fatigue: Mycelium can increase energy levels in humans in cases of post-viral fatigue etc.
- Nutritional Value: Mycelium is a source of essential nutrients, including vitamins, minerals, and amino acids, contributing to overall health and well-being (Rathore et al., 2019).
Notable Medicinal Mushrooms and Their Mycelium
Ganoderma lucidum (Reishi)
Reishi, also known as Lingzhi, is revered for its immune-boosting properties. The mycelium of Ganoderma lucidum is rich in polysaccharides and triterpenoids, which have been shown to enhance immune function, exhibit anti-cancer effects, and provide liver protection (Rathore et al., 2019).
Lentinula edodes (Shiitake)
Shiitake mushrooms are well known for their culinary uses, but their mycelium is also highly medicinal. Shiitake mycelium contains lentinan, a polysaccharide that has demonstrated potent anti-tumor and immunomodulating activities. Additionally, it exhibits anti-microbial and cholesterol-lowering properties (Rathore et al., 2019).
Hericium erinaceus (Lion’s Mane)
Lion’s Mane mushroom is notable for its neuroprotective properties. The mycelium produces compounds such as hericenones and erinacines, which stimulate nerve growth factor (NGF) synthesis, aiding in neurogenesis and improving cognitive function. This makes Lion’s Mane mycelium potentially beneficial in treating neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's (Rathore et al., 2019).
Cordyceps militaris
Cordyceps mycelium is known for its energy-boosting and anti-fatigue properties. It contains cordycepin, a bioactive compound that enhances physical performance, increases ATP production, and exhibits anti-tumor activities. Additionally, Cordyceps mycelium is used to support respiratory health and improve oxygen utilization (Rathore et al., 2019).
Trametes versicolor (Turkey Tail)
Turkey Tail mushrooms are recognized for their immune-modulating properties. The mycelium of Trametes versicolor contains polysaccharide-K (PSK) and polysaccharide-peptide (PSP), which have been extensively studied for their ability to boost immune function, particularly in cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy. These polysaccharides enhance the body's natural defense mechanisms and have shown promise in clinical trials for improving survival rates and quality of life in cancer patients (Rathore et al., 2019).
Grifola frondosa (Maitake)
Maitake, also known as "Hen of the Woods," is highly valued for its potent immune-enhancing effects. The mycelium of Grifola frondosa contains β-glucans, specifically D-fraction, which have demonstrated significant anti-tumor properties. Maitake mycelium enhances the activity of immune cells such as macrophages and natural killer cells, helping the body fight infections and cancer. It also exhibits potential benefits in regulating blood sugar levels and improving insulin sensitivity, making it useful in managing diabetes (Rathore et al., 2019).
Conclusion
The medicinal potential of mushroom mycelium is vast and well-documented. Specific mushrooms like Reishi, Shiitake, Lion’s Mane, Turkey Tail, Maitake, and Cordyceps offer a wide array of health benefits through their mycelium, from immune modulation to neuroprotection and anti-cancer properties. Submerged cultivation techniques provide an efficient way to harness these benefits, ensuring high-quality and potent mycelium. As research continues, the applications of these fungi in health and medicine will undoubtedly expand, offering new and innovative therapies for various ailments.
For further details and in-depth studies, refer to the comprehensive review by Rathore et al. (2019) on the medicinal importance of mushroom mycelium and its applications in functional foods.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1756464619301355