It is clear from the literature that lead is toxic, and more specifically, neurotoxic. It has generally been seen to cause a variety of symptoms according to the Mayo Clinic:
- High blood pressure.
- Joint and muscle pain.
- Difficulties with memory or concentration.
- Headache.
- Abdominal pain.
- Mood disorders.
- Reduced sperm count and abnormal sperm.
- Miscarriage, stillbirth or premature birth in pregnant women.
The vagus nerve is the primary interface with the outside world in the throat, lungs and gut. When we breath in lead, we damage the vagus nerve, when we swallow food or water with lead in it, we damage the vagus nerve. There is no safe level of lead.
Even in 1st world countries, lead is still very much a concern. Studies have shown that grains and vegetables grown in a variety of countries had dangerous levels of lead, but some fruits and pulses were at lower levels. This is due to soil contamination associated with poor management of the soil microbiome and due to local industries near farmland contaminating the region. Water contamination is still a problem too, although this is more common in 3rd world countries, even the USA and UK have numerous regions that have been prone to water contimination.
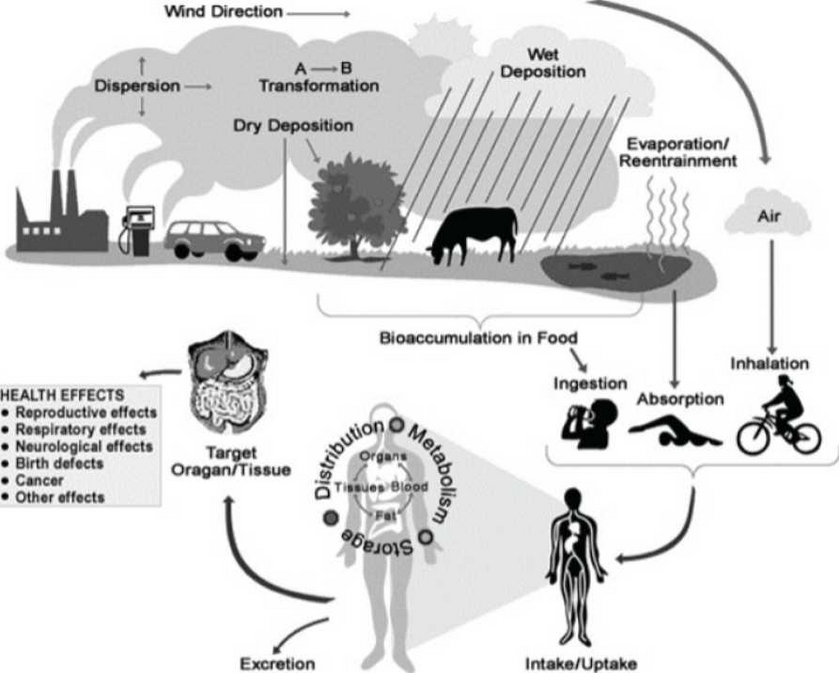
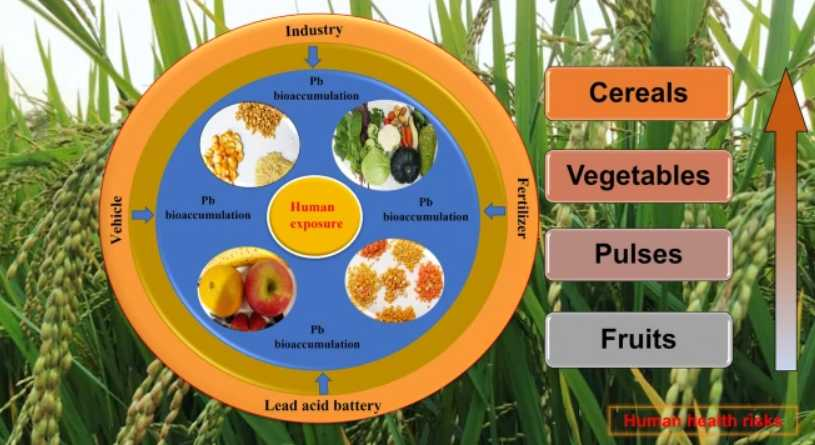
Consumption of certain types of food puts you at risk of exposure and increase absorption of lead. These include highly processed foods that include grains and refined vegetables in the ingredients, fast food like hamburgers, donuts, peanut butter and jelly sandwiches and cold cut meats increased the blood levels of lead. On the other hand, a diet rich in dairy products lowered the lead levels in the blood.
It is well established that lead exposure increases one's risk of dementia (Parkinson's and Alzheimer's), cardiovascular disease, cancer, kidney disease and numerous other neurological disorders. Its likely to be one of the leading causes of dysautonomia and POTS, not to mention vagus nerve damage more broadly.
The reason that lead is so damaging to nerves is due to its effect on the myelin sheath and it alters the voltage of the nerve due to diminishing its exclusion zone of water.
Measures to reduce lead:
- Only drink distilled drinking water
- Mainly consume meat, dairy and fruit (as these have the lowest levels of lead and contribute to lower blood lead levels)
- Avoid grains, tomatoes (high in lead) and most vegetables.
- Test your water at home in the bath, shower and where you wash your hands.
References
Dabrowska-Bouta B, Sulkowski G, Bartosz G, Walski M, Rafalowska U. Chronic lead intoxication affects the myelin membrane status in the central nervous system of adult rats. J Mol Neurosci. 1999 Aug-Oct;13(1-2):127-39. doi: 10.1385/JMN:13:1-2:127. PMID: 10691300.
Halmo L, Nappe TM. Lead Toxicity. 2023 Jul 4. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan–. PMID: 31082141.
Kubota K, Ito S, Ohta T, Nakazato Y, Ohga A. The inhibitory action of lead on mechanical responses of the proventricular smooth muscle in the chick. Jpn J Vet Res. 1994 Dec;42(3-4):109-17. PMID: 7745874.
Simões MR, Preti SC, Azevedo BF, Fiorim J, Freire DD Jr, Covre EP, Vassallo DV, Dos Santos L. Low-level Chronic Lead Exposure Impairs Neural Control of Blood Pressure and Heart Rate in Rats. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2017 Apr;17(2):190-199. doi: 10.1007/s12012-016-9374-y. PMID: 27272938.
Olufemi AC, Mji A, Mukhola MS. Potential Health Risks of Lead Exposure from Early Life through Later Life: Implications for Public Health Education. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Nov 30;19(23):16006. doi: 10.3390/ijerph192316006. PMID: 36498077; PMCID: PMC9741093.
TEUCHMANN JK. Wpłlyw zatrucia ołlowiem na odruchy rdzeniowe i nerw błledny [Effect of lead poisoning on medullary reflexes and on the vagus nerve]. Acta Physiol Pol. 1957;8(3-3a):545-8. Polish. PMID: 13532901.